Binary Search in C is one of the most important searching algorithms every beginner programmer must learn. It is widely used in competitive programming, technical interviews, and real-world software applications because of its speed and efficiency.

In this tutorial, you will learn Binary Search in C from scratch, even if you are completely new to programming.
What is Binary Search in C?
Binary Search is an efficient algorithm used to search an element in a sorted array.
Instead of checking each element one by one (like Linear Search), Binary Search:
- Divides the array into two halves
- Compares the middle element with the target value
- Eliminates half of the array in each step
This makes Binary Search extremely fast.
Important Condition for Binary Search
⚠️ Binary Search works only on a sorted array
Example of a sorted array:
2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 23, 38
Example of an unsorted array (Binary Search will not work):
8, 2, 16, 5, 23, 12
Why Use Binary Search Instead of Linear Search?
| Search Method | Approach | Speed |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Search | Checks every element | Slow |
| Binary Search | Divides array into halves | Very Fast |
Binary Search is ideal when working with large datasets.
How Binary Search Works (Step-by-Step)
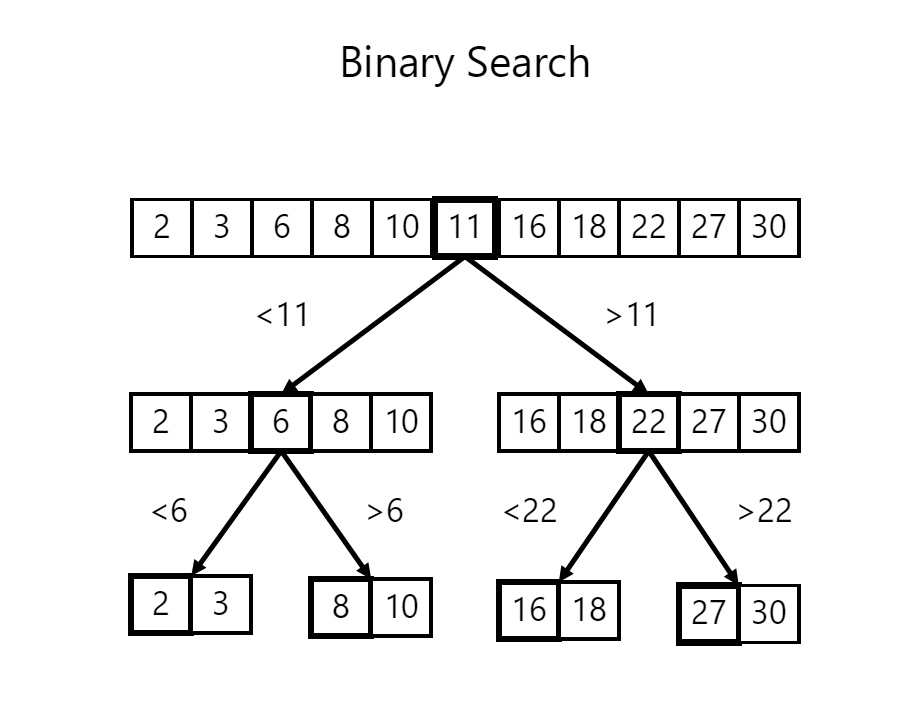
Consider this sorted array:
Index: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Array: 3 7 12 18 25 31 40
We want to search for 18.
Step 1: Find the middle element
mid = (start + end) / 2 mid = (0 + 6) / 2 = 3
Middle element = 18
Step 2: Compare
- If middle element equals the key → Element found
- If key is smaller → search left half
- If key is larger → search right half
Since 18 == 18, the search stops successfully.
Binary Search Algorithm in C (Simple Steps)
- Initialize
start = 0 - Initialize
end = size - 1 - Repeat while
start <= end - Calculate middle index
- Compare middle element with key
- Move left or right accordingly
Binary Search Program in C
#include <stdio.h>
int binarySearch(int arr[], int size, int key) {
int start = 0;
int end = size - 1;
while (start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == key)
return mid;
else if (key < arr[mid])
end = mid - 1;
else
start = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30};
int size = 6;
int key = 20;
int result = binarySearch(arr, size, key);
if (result != -1)
printf("Element found at index %d", result);
else
printf("Element not found");
return 0;
}
Explanation of Binary Search Code in C
start→ first index of the arrayend→ last index of the arraymid→ middle position- If
arr[mid] == key→ element found - If
key < arr[mid]→ search left half - If
key > arr[mid]→ search right half
The loop continues until the element is found or the search space becomes empty.
Output
Element found at index 3
Time Complexity of Binary Search
| Case | Time Complexity |
|---|---|
| Best Case | O(1) |
| Average Case | O(log n) |
| Worst Case | O(log n) |
👉 O(log n) means the algorithm is extremely fast, even for large arrays.
Advantages of Binary Search
- Faster than Linear Search
- Efficient for large datasets
- Reduces search space by half every step
- Commonly asked in interviews
Disadvantages of Binary Search
- Works only on sorted arrays
- Not suitable for frequently changing data
- Requires random access to elements
When to Use Binary Search?
✅ When data is sorted
✅ When performance is critical
✅ When working with large datasets
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is Binary Search faster than Linear Search?
Yes, Binary Search is much faster, especially for large arrays.
Can Binary Search be used on unsorted arrays?
No, the array must be sorted first.
Is Binary Search recursive or iterative?
Binary Search can be implemented using both methods.
Conclusion
Binary Search in C is a fundamental algorithm that every beginner should master. It improves problem-solving skills and introduces the powerful divide-and-conquer technique.
Once you understand Binary Search, learning advanced algorithms becomes much easier.
